Amur
| Amur Heilong | |
|---|---|
 | |
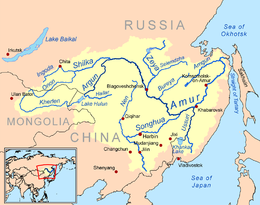 Map of the Amur watershed | |
| Etymology | From Mongolian: amar ("rest") |
| Location | |
| Countries | |
| Cities | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Onon-Shilka |
| • location | Khan Khentii Strictly Protected Area, Khentii Province, Mongolia |
| • coordinates | 48°48′59″N 108°46′13″E / 48.81639°N 108.77028°E |
| • elevation | 2,045 m (6,709 ft) |
| 2nd source | Argun |
| • location | Greater Khingan, Hulunbuir, China |
| • coordinates | 49°56′13″N 122°27′54″E / 49.937°N 122.465°E |
| Source confluence | |
| • location | Near Pokrovka, Russia |
| • coordinates | 53°19′58″N 121°28′37″E / 53.33278°N 121.47694°E |
| • elevation | 303 m (994 ft) |
| Mouth | Strait of Tartary |
• location | Near Nikolayevsk-on-Amur, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia |
• coordinates | 52°56′50″N 141°05′02″E / 52.94722°N 141.08389°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 2,824 km (1,755 mi)[1][2] (Amur–Argun–Hailar: 4,444 km)[2] |
| Basin size | 1,855,000 km2 (716,000 sq mi)[1] 2,129,700 km2 (822,300 sq mi)(with undrained areas)[2] |
| Width | |
| • maximum | 5,000 m (16,000 ft) |
| Depth | |
| • maximum | 57 m (187 ft) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Near mouth |
| • average | (Period: 2002–2020)12,360 m3/s (390 km3/a)[3]
(Period: 1896–2004)11,330 m3/s (400,000 cu ft/s)[4] [2] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Bogorodskoye |
| • average | (Period: 2008–2019)11,459 m3/s (404,700 cu ft/s)[5]
(Period: 1896–2004)10,100 m3/s (360,000 cu ft/s)[4] [6] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Komsomolsk-on-Amur |
| • average | (Period: 2012–2019)10,259 m3/s (362,300 cu ft/s)[5] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Khabarovsk |
| • average | (Period: 2008–2018)8,384 m3/s (296,100 cu ft/s)[5]
(Period: 1896–2004)8,360 m3/s (295,000 cu ft/s)[4] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Blagoveshchensk |
| • average | (Period: 1971–2000)2,859.1 m3/s (100,970 cu ft/s)[7] |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Strait of Tartary (Sea of Okhotsk) |
| River system | Amur River |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Shilka, Amazar, Oldoy, Zeya, Bureya, Arkhara, Bidzhan, Bira, Tunguska, Bolon, Gorin, Bichi, Amgun, Palvinskaya |
| • right | Argun, Emuer, Huma, Xun, Kuerbin, Songhua, Nongjiang, Ussuri, Sita, Nemta, Anyuy, Gur, Yai |
 | |
| Amur | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russian name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Russian | река Амур | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 黑龙江 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 黑龍江 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Heilung Kiang | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Black Dragon River" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manchu script | ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ ᡠᠯᠠ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Romanization | Sahaliyan ula | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amur summary route map | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note: Distances are in kilometers. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Amur River (Russian: река Амур) or Heilong River (Chinese: 黑龙江)[8] is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is 2,824 km (1,755 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 1,855,000 km2 (716,000 sq mi).[1][9] If including its main stem tributary, the Argun, the Amur is 4,444 km (2,761 mi) long,[9][2] making it the world's tenth longest river.
The Amur is an important river for the aquatic fauna of Northeast Asia. The river basin is home to a variety of large predatory fish such as northern snakehead, Amur pike, taimen, Amur catfish, predatory carp and yellowcheek,[10] as well as several species of trout and anadromous salmonids. The largest fish species in the Amur is the kaluga, a sturgeon that is one of the largest freshwater fish in the world, attaining a length as great as 5.6 m (18 ft).[11] It is also home to the northernmost populations of the Amur softshell turtle[12] and Indian lotus.[13]
Name
[edit]The Russian name Amur may come from the Tungusic term for “river”.[citation needed] Tungusic peoples are an ethno-linguistic group formed by the speakers of Tungusic languages (or Manchu–Tungus languages). They are native to Siberia and Northeast Asia.[14]
The etymology of the name Amur is unknown. One theory dictates that it comes to Russian through either the Evenki word amur or the Even word amar, both meaning "river" in their respective Tungusic languages. However, it is unclear whether Russian borrowed the name Amur from either Tungusic language rather than the other way around. An alternative theory suggests that Amur comes from the Mongolic language Dagur's, word for "big river," mur.[15]
Its ancient Chinese names were Yushui, Wanshui and Heishui,[16] with the latter name, meaning "black water", being the basis of the modern Chinese name Heilongjiang or "Black Dragon River", while the Manchurian name Sahaliyan Ula, the Mongolian names "Amar mörön" (Cyrillic: Амар мөрөн) originates from the name "Amar" meaning to rest and Khar mörön (Cyrillic: Хар мөрөн) mean Black River.[1]
Course
[edit]The river rises in the hills in the western part of Northeast China at the confluence of its two major affluents, the Shilka and the Argun (or Ergune), at an elevation of 303 metres (994 ft).[17] It flows east forming the border between China and Russia, and slowly makes a great arc to the southeast for about 400 kilometres (250 mi), receiving many tributaries and passing many small towns. At Huma, it is joined by a major tributary, the Huma He.[18] Afterwards it continues to flow south until, between the cities of Blagoveshchensk in Russia and Heihe in China, it widens significantly as it is joined by one of its most important tributaries the Zeya.[19]
The Amur arcs to the east and turns southeast again at the confluence with the Bureya, then does not receive another significant tributary for nearly 250 kilometres (160 mi) before its confluence with its largest tributary, the Songhua, at Tongjiang. At the confluence with the Songhua the river turns northeast, now flowing towards Khabarovsk, where it joins the Ussuri and ceases to define the Russia–China border. Now the river spreads out dramatically into a braided character, flowing north-northeast through a wide valley in eastern Russia, passing Amursk and Komsomolsk-on-Amur. The valley narrows after about 200 kilometres (120 mi) and the river again flows north onto plains at the confluence with the Amgun. Shortly after, the Amur turns sharply east and into an estuary at Nikolayevsk-on-Amur, about 20 kilometres (12 mi) downstream of which it flows into the Strait of Tartary.[20]
During years with heavy precipitation, the Amur river system is connected with the Kherlen river. The normally exit−less endorheic lake Hulun Lake, into which Kherlen flows, will overflow at its northern shore through the arroyo of Mutnaya Protoka, and the water will meet the Argun River (Ergune) after about 30 kilometres (19 mi). The Amur Basin of the Kherlen−Argun−Amur River system has a total length of 5,052 km (3,139 mi) to its river mouth on the Sea of Okhotsk.[21]
Tributaries
[edit]The largest tributaries of the Amur are, from source to mouth:[9][22]
There are also numerous lakes in the floodplain of the Amur. Some of the largest ones are Bolon, Khummi and Udyl.[23]
The main tributaries from the mouth:
| Left
tributary |
Right
tributary |
Length
(km) |
Basin size
(km2) |
Average discharge
(m3/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amur (Heilongjiang) | 4,444 | 2,129,700 | 12,791 | |
| Lower Amur | ||||
| Protoka Palvinskaya | 34 | 6,675.4 | 75.7 | |
| Amgun | 723 | 54,602.6 | 660 | |
| Akcha | 58 | 987.7 | 11.1 | |
| Protoka Ukhta–Bichi | 336 | 12,910.2 | 46.2 | |
| Poto | 22 | 845.7 | 5.8 | |
| Kadi | 52 | 645.9 | 7.6 | |
| Yai | 118 | 3,865.4 | 28.8 | |
| Limuri | 168 | 4,125.3 | 16.4 | |
| Salasu | 68 | 1,205 | 6.9 | |
| Pisuy | 59 | 856.2 | 2.7 | |
| Machtovaya | 103 | 1,477.2 | 15.4 | |
| Gorin | 390 | 21,953.6 | 150 | |
| Silinka | 78 | 974.1 | 6.4 | |
| Bolin | 43 | 1,219.8 | 14.1 | |
| Gur | 349 | 11,635.4 | 226.3 | |
| Elban | 99 | 1,756.8 | 27 | |
| Bolon–Harpi | 239 | 13,129.7 | 245.6 | |
| Gili | 22 | 1,328 | 25.1 | |
| Khoydur | 41 | 571.2 | 11.7 | |
| Anyuy | 393 | 12,528.7 | 298.4 | |
| Pikhtsa | 90 | 872.9 | 19.1 | |
| Khar | 66 | 1,307.3 | 28 | |
| Nemta (Neptu) | 230 | 6,290 | 143.5 | |
| Sita (Strelka) | 105 | 3,315.4 | 67.4 | |
| Levaya | 421.4 | 9.9 | ||
| Darga | 50 | 1,628 | 36.8 | |
| Tunguska–Urmi | 544 | 30,070.2 | 595.6 | |
| Ussuri (Wusulijiang) | 897 | 195,047.4 | 1,620 | |
| Middle Amur | ||||
| Krestovaya | 70 | 1,361.2 | 18.6 | |
| Nongjiang | 4,469.9 | 30.1 | ||
| Petrovskaya | 62 | 996.8 | 11.4 | |
| Bira | 424 | 9,279.1 | 84.2 | |
| Malaya Bira | 150 | 1,946 | 13 | |
| Penghua | 2,740.5 | 13.6 | ||
| Solonechnaya | 52 | 963.4 | 4.7 | |
| Sungari (Songhua) | 1,927 | 552,629.8 | 2,591 | |
| Wanyan | 163.9 | 1,815.1 | 9 | |
| Bidzhan | 274 | 7,335.9 | 46.2 | |
| Dobraya | 58 | 1,996.6 | 10.7 | |
| Samara | 105 | 1,560.7 | 9.2 | |
| Pompeyevka | 71 | 635.6 | 3.9 | |
| Jiayin | 2,109.1 | 12.3 | ||
| Wulaga | 1,213.5 | 7 | ||
| Khingan | 93 | 2,012.6 | 13.3 | |
| Uril | 105 | 1,160.4 | 7.1 | |
| Jielie | 1,005.6 | 5.7 | ||
| Wuyun | 2,239.4 | 12 | ||
| Arkhara | 155 | 8,643.4 | 82.1 | |
| Bureya | 739 | 70,141.2 | 932 | |
| Raychikha | 97 | 760 | 3.8 | |
| Kupriyanikha | 55 | 689 | 3.4 | |
| Kuerbin | 221 | 5,826.2 | 22.2 | |
| Xun (Hsünho) | 15,624.8 | 62.6 | ||
| Zavitaya | 262 | 2,835.1 | 13.7 | |
| Dim | 1,348 | 6.5 | ||
| Topkocha | 44 | 978.8 | 4.5 | |
| Gilchin | 90 | 1,492.7 | 6.7 | |
| Gongbiela | 38.8 | 2,678.5 | 10.9 | |
| Manga (Big Alim) | 58 | 733.1 | 3.4 | |
| Shijin | 759 | 3.2 | ||
| Zeya | 1,232 | 232,076.5 | 1,807 | |
| Upper Amur | ||||
| Fabiela | 2,916.9 | 11.2 | ||
| Fanqniuhe | 747.8 | 2.9 | ||
| Guran | 55 | 781.3 | 3 | |
| Kuanhe | 2,159 | 6.7 | ||
| Belaya | 77 | 1,069.7 | 3.7 | |
| Bereya | 146 | 2,013.5 | 6.3 | |
| Huma | 542 | 31,029.4 | 130 | |
| Belaya | 102 | 1,176.8 | 3.6 | |
| Ulmin | 67 | 985.8 | 3.2 | |
| Borya (Onon) | 14 | 1,109.5 | 3.6 | |
| Gerbelik (Herbelic) | 43 | 702.6 | 2.4 | |
| Olga | 158 | 2,905.3 | 10.1 | |
| Burinda | 80 | 2,371.4 | 7.7 | |
| Xiergenqi | 3,807.6 | 12.5 | ||
| Pangu | 165 | 3,631.5 | 11.4 | |
| Osezinha | 84 | 1,129.8 | 3.6 | |
| Emuer | 469 | 16,106.1 | 46.2 | |
| Bolshoy Never | 134 | 2,211.1 | 7.1 | |
| Oldoy | 287 | 9,878.2 | 38.3 | |
| Urusha | 200 | 3,442.3 | 13.4 | |
| Omutnaya | 171 | 2,163.1 | 7.6 | |
| Urka | 161 | 1,897.3 | 6.9 | |
| Amazar | 290 | 11,031 | 37.9 | |
| Shilka (1) | 555 | 206,000 | 571.1 | |
| Argun (Erguna) (2) | 944 | 300,977 | 408.5 | |
| Argun main tributaries | ||||
| Enhehada | 2,130.8 | 4.5 | ||
| Gazimur | 592 | 12,047.5 | 32.4 | |
| Budyumkan | 91 | 1,410.4 | 2.8 | |
| Uryumkan | 226 | 4,337.5 | 9.3 | |
| Wumahe (Uma) | 1,817.3 | 3.8 | ||
| Urov | 290 | 4,288.8 | 10.3 | |
| Abahe (Aba) | 2,383 | 5.2 | ||
| Jiliu | 468 | 15,771.7 | 47.2 | |
| Moridaga | 2,664.2 | 7 | ||
| Nizhnyaya Borzya | 1,793.2 | 5.2 | ||
| Srednyaya Borzya | 118 | 1,632.2 | 4.3 | |
| Verkhnyaya Borzya | 153 | 4,028.8 | 10.7 | |
| Urulyunguy | 189 | 8,924.1 | 17.9 | |
| Derbur | 6,779.3 | 17.7 | ||
| Genhe (Kenho) | 400 | 15,787.8 | 58.1 | |
| Dalan Orom (Xinkai)–Kherlen (3) | 1,284 | 140,000 | 40.7 | |
| Hailar | 555 | 54,800 | 139.1 | |
| Hailar main tributaries | ||||
| Morgele | 319 | 4,936.4 | 12.4 | |
| Yimin | 360 | 21,332.1 | 39.6 | |
| Moheri Tugaole | 956.1 | 3.1 | ||
| Teni | 1,401.8 | 4.3 | ||
| Miandu | 6,659.8 | 28 | ||
| Kudur | 3,461.6 | 13.7 | ||
| Dayan (Hailar) | 121 | 3,325.4 | 13 | |
| Endorheic basin | ||||
| Ulz | 420 | 35,000 | 7.7 | |
| Source: [24][7][2] | ||||
(1)Amur–Shilka–Onon: 4,354 km; (2)Amur–Argun–Hailar–Dayan: 4,444 km; (3)Amur–Argun–Dalan Orom–Kherlen: 5,052 km;
History and context
[edit]Many historical references distinguish two geopolitical entities in the area of the Amur: Manchuria (Northeast China) and Outer Manchuria. The Chinese province of Heilongjiang on the south bank of the river takes its name from the river, as does the Russian Amur Oblast on the north bank. The native Manchu people and their Qing Empire of China, who regarded this river as sacred,[citation needed] use the name Sahaliyan Ula (Black River).
The Amur is an important symbol of, and geopolitical factor in, Chinese–Russian relations. The Amur became especially prominent in the period of the Sino–Soviet political split of 1956–1966.
For many[quantify] centuries, inhabitants of the Amur Valley comprised the Tungusic (Evenki, Solon, Ducher, Jurchen, Nanai, Ulch), Mongol (Daur) people, some Ainu and, near its mouth, the Nivkhs.[25] For many of these groups, fishing in the Amur and its tributaries was the main source of their livelihood. Until the 17th century these peoples were not known to Europeans, and little known to the Han Chinese, who sometimes collectively described them as the Wild Jurchens. The Chinese-language term Yúpí Dázi 魚皮韃子 ("Fish-skin Tatars") came to apply to the Nanais and related groups as well, owing to their traditional clothes made of fish skins.[26]

The Mongols, ruling the region as the Yuan dynasty, established a tenuous military presence on the lower Amur in the 13th and 14th centuries; ruins of a Yuan-era temple have been excavated near the village of Tyr.[27]
During the reigns of the Yongle and Xuande Emperors (early-15th century), the Ming dynasty reached the Amur in their drive to establish control over the lands adjacent to the Ming Empire to the northeast, which would later become known as Manchuria. Expeditions headed by the eunuch Yishiha reached Tyr several times between 1411 and the early 1430s, re-building (twice) the Yongning Temple and obtaining at least the nominal allegiance of the lower Amur's tribes to the Ming government.[28][29] Some sources report also a Chinese presence during the same period on the middle Amur – a fort existed at Aigun for about 20 years during the Yongle era on the left (northwestern) shore of the Amur downstream from the mouth of the Zeya River. This Ming Dynasty Aigun was located on the opposite bank to the later Aigun that was later relocated during the Qing Dynasty.[30] In any event, the Ming presence on the Amur was as short-lived as it was tenuous; soon after the end of the Yongle era, the Ming dynasty's frontiers retreated to southern Manchuria. [citation needed]
Chinese cultural and religious influence such as Chinese New Year, the "Chinese god", Chinese motifs like the dragon, spirals, scrolls, and material goods like agriculture, husbandry, heating, iron cooking-pots, silk, and cotton spread among Amur natives such as the Udeghes, Ulchis, and Nanais.[31]
Russian Cossack expeditions led by Vassili Poyarkov and Yerofey Khabarov explored the Amur and its tributaries in 1643–44 and 1649–51, respectively. The Cossacks established the fort of Albazin on the upper Amur, at the site of the former capital of the Solons.[citation needed]

At the time, the Manchus were busy with conquering China; but a few decades later, during the Kangxi era of 1661–1722, they turned their attention to their north-Manchurian backyard. Aigun was re-established near the supposed Ming site in about 1683–84, and a military expeditions went upstream to dislodge the Russians, whose Albazin establishment deprived the Manchu rulers of the tribute of sable pelts that the Solons and Daurs of the area would supply otherwise.[32] Albazin fell during a short military campaign in 1685. The Treaty of Nerchinsk, concluded in 1689, marked the end of the hostilities: it left the entire Amur valley, from the convergence of the Shilka and the Ergune downstream, in Chinese hands.[citation needed]
Fedor Soimonov was sent to map the then little explored area of the Amur in 1757. He mapped the Shilka, which was partly in Chinese territory, but was turned back when he reached its confluence with the Argun.[33] The Russian proselytization of Orthodox Christianity to the indigenous peoples along the Amur was viewed as a threat by the Qing.[34]

The Amur region remained a relative backwater of the Qing Empire for the next century and a half, with Aigun being practically the only major town on the river. Russians re-appeared on the river in the mid-19th century, forcing the Manchus to yield all lands north of the river to the Russian Empire by the Treaty of Aigun (1858). Lands east of the Ussuri and the lower Amur were acquired by Russia as well, by the Convention of Peking (1860).[35]
Bridges and tunnels
[edit]| Amur | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 黑龍江 | ||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 黑龙江 | ||||||
| Literal meaning | "Black Dragon River" | ||||||
| |||||||
| Alternative Chinese name | |||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 阿穆爾河 | ||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 阿穆尔河 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||
| Mongolian Cyrillic | Хар Мөрөн / Амар Мөрөн | ||||||
| |||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||
| Manchu script | ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ ᡠᠯᠠ | ||||||
| Romanization | Sahaliyan Ula | ||||||
| Russian name | |||||||
| Russian | Амур | ||||||
| Romanization | Amur | ||||||
The first permanent bridge across the Amur, the Khabarovsk Bridge with an overall length of 2,590 metres (8,500 ft), was completed in 1916, allowing the trains on the Trans-Siberian Railway to cross the river year-round without using ferries or rail tracks on top of the river ice. In 1941 a railway tunnel was added as well.[citation needed]
Later, a combined road and rail bridge over the Amur at Komsomolsk-on-Amur (1975; 1400 m) and the road and rail Khabarovsk Bridge (1999; 3890 m) were constructed.
The Tongjiang-Nizhneleninskoye railway bridge was proposed in 2007 by Valery Solomonovich Gurevich, the vice-chairman of the Jewish Autonomous Oblast in Russia. The railway bridge over the Amur will connect Tongjiang with Nizhneleninskoye, a village in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast.[36] The Chinese portion of the bridge was finished in July 2016.[37] In December 2016, work began on the Russian portion of the bridge. Completion of structural link between the two sides of the bridge was completed in March 2019.[38][39] Opening to rail traffic has been repeatedly delayed, with the December 2019 estimate being "the end of 2020",[40] and then 3rd quarter of 2021.[41]
Wildlife
[edit]
It is believed there are at least 123 species of fish from 23 families inhabiting the Amur. The majority are of the Gobioninae subfamily of Cypriniformes, followed in number by Salmonidae. Several of the species are endemic. Pseudaspius and Mesocottus are monotypic genera found only in the Amur and some nearby coastal rivers.[16] Other animals inhabiting this region include the Amur falcon, Amur leopard and Amur tiger; while some notable local flora include Amur cork tree, Amur maple and the Amur honeysuckle.[42]
Four species of the Acipenseridae family can be found: the kaluga, Amur sturgeon, Sakhalin sturgeon and sterlet. The Kaluga and Amur sturgeon are endemic. The sterlet was introduced from the Ob in the 1950s.[43] This region is home to the Kaluga fish (Acipenseriformes).
Direction
[edit]Flowing across northeast Asia for over 4,444 kilometres (2,761 mi) (including its two tributaries), from the mountains of northeastern China to the Sea of Okhotsk (near Nikolayevsk-na-Amure), it drains a remarkable watershed that includes diverse landscapes of desert, steppe, tundra, and taiga, eventually emptying into the Pacific Ocean through the Strait of Tartary, where the mouth of the river faces the northern end of the island of Sakhalin.[citation needed]

The Amur has always been closely associated with the island of Sakhalin at its mouth, and most names for the island, even in the languages of the indigenous peoples of the region, are derived from the name of the river: "Sakhalin" derives from a Tungusic dialectal form cognate with Manchu sahaliyan ("black", as in sahaliyan ula, "Black River"), while Ainu and Japanese "Karaputo" or "Karafuto" is derived from the Ainu name of the Amur or its mouth. Anton Chekhov vividly described the Amur in writings about his journey to Sakhalin Island in 1890.[citation needed]
The average annual discharge varies from 6,000 cubic metres per second (210,000 cu ft/s) (1980) to 12,000 cubic metres per second (420,000 cu ft/s) (1957), leading to an average 9,819 cubic metres per second (346,800 cu ft/s) or 310 cubic kilometres (74 cu mi) per year. The maximum runoff measured occurred in Oct 1951 with 30,700 cubic metres per second (1,080,000 cu ft/s) whereas the minimum discharge was recorded in March 1946 with a mere 514 cubic metres per second (18,200 cu ft/s).[44]
See also
[edit]- Geography of China
- Geography of Russia
- Sino-Soviet border conflict
- List of longest undammed rivers
- Sixty-Four Villages East of the Heilong Jiang
- Amur Military Flotilla
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Muranov, Aleksandr Pavlovich; Greer, Charles E.; Owen, Lewis. "Amur River". Encyclopædia Britannica (online ed.). Archived from the original on 2016-05-21. Retrieved 2016-08-31.
- ^ a b c d e f Eugene A., Simonov; Thomas D., Dahmer (2008). Amur-Heilong River Basin Reader (PDF). Ecosystems. ISBN 9789881722713.
- ^ Andrey, Andreev (2023). "Intra-Seasonal Variability of Sea Level on the Southwestern Bering Sea Shelf and Its Impact on the East Kamchatka and East Sakhalin Currents". Remote Sensing. 15 (20): 4984. Bibcode:2023RemS...15.4984A. doi:10.3390/rs15204984.
- ^ a b c "DRAINAGE BASINS OF THE SEA OF OKHOTSK AND SEA OF JAPAN" (PDF). pp. 60–67.
- ^ a b c Peter, Bauer-Gottwein; Elena, Zakharova; Monica, Coppo Frías; Heidi, Ranndal; Karina, Nielsen; Linda, Christoffersen (2023). "A hydraulic model of the Amur River informed by ICESat-2 elevation". Hydrological. 68 (14): 2027-2041. Bibcode:2023HydSJ..68.2027B. doi:10.1080/02626667.2023.2245811.
- ^ "Variations of the Present-Day Annual and Seasonal Runoff in the Far East and Siberia with the Use of Regional Hydrological and Global Climate Models" (PDF).
- ^ a b "Heilong Jiang-Amur".
- ^ Liaoning province's archive, Manchu Veritable Record Upper Vol《滿洲實錄上函/manju-i yargiyan kooli dergi dobton》
- ^ a b c Амур (река в Азии), Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- ^ FishBase: Species in Amur. Archived 2019-02-18 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ C. Michael Hogan. 2012. Amur River. Encyclopedia of Earth. Archived November 30, 2012, at the Wayback Machine Topic ed. Peter Saundry
- ^ Farkas, B., T. Ziegler, C.T. Pham, A.V. Ong and U. Fritz (2019). A new species of Pelodiscus from northeastern Indochina (Testudines, Trionychidae). ZooKeys 824: 71-86. doi:10.3897/zookeys.824.31376
- ^ Yi Zhang; Xu Lu; Shaoxiao Zeng; Xuhui Huang; Zebin Guo; Yafeng Zheng; Yuting Tian; Baodong Zheng (2015). "Nutritional composition, physiological functions and processing of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds: a review". Phytochem Rev. 14 (3): 321–334. doi:10.1007/s11101-015-9401-9
- ^ Jia, Mingming; Mao, Dehua; Wang, Zongming; Ren, Chunying; Zhu, Qiande; Li, Xuechun; Zhang, Yuanzhi (1 October 2020). "Tracking long-term floodplain wetland changes: A case study in the China side of the Amur River Basin". International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation. 92: 102185. Bibcode:2020IJAEO..9202185J. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2020.102185. ISSN 1569-8432. S2CID 221044242.
- ^ Piispanen, Peter (2019). "Languages in Contact: Solon and Dagur".
- ^ a b The fishes of the Amur River:updated check-list and zoogeography Archived 2020-02-04 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Source elevation derived from Google Earth
- ^ Lasserre, Frédéric (27 June 2003). "The Amur River border. Once a symbol of conflict, could it turn into a water resource stake?". Cybergeo. doi:10.4000/cybergeo.4141. hdl:20.500.11794/790. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ Mao, Dehua; Tian, Yanlin; Wang, Zongming; Jia, Mingming; Du, Jia; Song, Changchun (15 February 2021). "Wetland changes in the Amur River Basin: Differing trends and proximate causes on the Chinese and Russian sides". Journal of Environmental Management. 280: 111670. Bibcode:2021JEnvM.28011670M. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111670. ISSN 0301-4797. PMID 33218828. S2CID 227100672. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 899.
- ^ "Untitled Document".
- ^ "Река Амур in the State Water Register of Russia". verum.wiki (in Russian).
- ^ "Water of Russia - Khabarovsk Krai".
- ^ "Поиск по данным государственного водного реестра".
- ^ Peter Bellwood; Immanuel Ness (10 November 2014). The Global Prehistory of Human Migration. John Wiley & Sons. p. 227. ISBN 978-1-118-97059-1.
- ^ Hölzl, Andreas (2018). "Udi, Udihe, and the language(s) of the Kyakala". International Journal of Diachronic Linguistics and Linguistic Reconstruction. 15: 111–146.
- ^ Головачев В. Ц. (V. Ts. Golovachev), «Тырские стелы и храм „Юн Нин“ в свете китайско-чжурчжэньских отношений XIV—XV вв.» Archived 2009-02-23 at the Wayback Machine (The Tyr Stelae and the Yongning Temple viewed in the context of Sino-Jurchen relations of the 14-15th centuries) Этно-Журнал, 2008-11-14. (in Russian)
- ^ L. Carrington Godrich, Chaoying Fang (editors), "Dictionary of Ming Biography, 1368–1644". Volume I (A-L). Columbia University Press, 1976. ISBN 0-231-03801-1
- ^ Shih-Shan Henry Tsai, "Perpetual Happiness: The Ming Emperor Yongle". Published by University of Washington Press, 2002. ISBN 0-295-98124-5 Partial text Archived 2017-01-10 at the Wayback Machine on Google Books. pp. 158-159.
- ^ Du Halde, Jean-Baptiste (1735). Description géographique, historique, chronologique, politique et physique de l'empire de la Chine et de la Tartarie chinoise. Vol. IV. Paris: P.G. Lemercier. pp. 15–16. Archived from the original on 2009-07-02. Retrieved 2009-04-01. Numerous later editions are available as well, including one on Google Books Archived 2017-01-10 at the Wayback Machine. Du Halde refers to the Yongle-era fort, the predecessor of Aigun, as Aykom. There seem to be few, if any, mentions of this project in other available literature.
- ^ Forsyth 1994 Archived 2016-05-14 at the Wayback Machine, p. 214.
- ^ Du Halde (1735), pp. 15-16
- ^ Foust, Muscovite and Mandarin p. 245-250
- ^ Kim 金由美, Loretta E. (2013). "Saints for Shamans? Culture, Religion and Borderland Politics in Amuria from the". Central Asiatic Journal. 56: 169–202 [169]. JSTOR 10.13173/centasiaj.56.2013.0169.
- ^ "The Convention of Peking of 1860 is concluded". Presidential Library. Retrieved 2022-07-12.
- ^ Proposed bridge to boost bilateral trade Archived 2013-05-28 at the Wayback Machine, China Daily, June 19, 2007.
- ^ Andrew Higgins (July 16, 2016). "An Unfinished Bridge, and Partnership, Between Russia and China". The New York Times. Archived from the original on July 16, 2016. Retrieved July 17, 2016.
- ^ "Russia Completes Construction of First-Ever Rail Bridge to China", The Moscow Times, March 21, 2019, retrieved November 16, 2020
- ^ Россия и Китай соединили железнодорожный мост через Амур [Russia and China connected a railway bridge across the Amur] (in Russian), RBK Group, March 21, 2019, retrieved November 16, 2020
- ^ "Railway bridge over Amur river to China will be built by end of 2020, envoy says". TASS. Retrieved November 16, 2020.
- ^ "Новости Хабаровска".
- ^ Sokolova, Galina V.; Verkhoturov, Andrei L.; Korolev, Sergei P. (June 2019). "Impact of Deforestation on Streamflow in the Amur River Basin". Geosciences. 9 (6): 262. Bibcode:2019Geosc...9..262S. doi:10.3390/geosciences9060262. ISSN 2076-3263.
- ^ Endemic sturgeons of the Amur River: kaluga, Huso dauricus, and Amur sturgeon, Acipenser schrencki Archived 2020-02-04 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Amur at Komsomolsk". UNESCO. Archived from the original on 2012-08-12. Retrieved 2008-08-14.
Further reading
[edit]- Bisher, Jamie (2006). White Terror: Cossack Warlords of the Trans-Siberian. Routledge. ISBN 1135765952. Retrieved 24 April 2014. also ISBN 1135765960
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 899.
- Forsyth, James (1994). A History of the Peoples of Siberia: Russia's North Asian Colony 1581-1990 (illustrated, reprint, revised ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521477719. Retrieved 24 April 2014.
- Kang, Hyeokhweon. Shiau, Jeffrey (ed.). "Big Heads and Buddhist Demons: The Korean Military Revolution and Northern Expeditions of 1654 and 1658" (PDF). Emory Endeavors in World History. 4: Transnational Encounters in Asia (2013 ed.): 1–22. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-01-15. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- Kim 金, Loretta E. 由美 (2012–2013). "Saints for Shamans? Culture, Religion and Borderland Politics in Amuria from the Seventeenth to Nineteenth Centuries". Central Asiatic Journal. 56. Harrassowitz Verlag: 169–202. JSTOR 10.13173/centasiaj.56.2013.0169.
- McAleavy, Henry. "China and the Amur Provinces" History Today (June 1964) 14#6 pp 381–390.
- Stephan, John J. (1996). The Russian Far East: A History (illustrated, reprint ed.). Stanford University Press. ISBN 0804727015.
- Thubron, Colin (2021). The Amur River: Between Russia and China. London: Chatto & Windus.
- Ziegler, Dominic (2015). Black Dragon River: A Journey Down the Amur River Between Russia and China.
External links
[edit]- Amur-Heilong River Basin Information Center - maps, GIS data, environmental data
- Information and a map of the Amur’s watershed
- Amur basin
- Rivers of China
- Rivers of the Russian Far East
- Border rivers
- China–Russia border
- International rivers of Asia
- Geography of Northeast Asia
- Geography of Northeast China
- Rivers of Inner Mongolia
- Rivers of Khabarovsk Krai
- Rivers of Heilongjiang
- Rivers of Amur Oblast
- Rivers of Zabaykalsky Krai
- Rivers of Jewish Autonomous Oblast
- Amur River
